
Worms in humans, the symptoms and treatment of which will be indicated by a doctor, in the human body are caused by two types of worms: round (nematodes) and flat (trematodes and tapeworms). Each of the parasites causes significant harm to the body, especially if proper treatment has not been provided in time.
Be sure to wash your hands when you get home, and also rinse vegetables or fruits under warm or hot running water, as parasite eggs are likely to be found in them. Products such as fish meat or livestock must necessarily undergo heat treatment. Under the action of high temperatures, the meat gets rid of the eggs of various helminths and can be made suitable for eating.
Varieties of roundworms.
Pinworms are small grayish-white parasitic flatworms that cause enterobiasis.
Such parasites enter the human body in the following ways:
- alimentary (through the oral cavity);
- through unwashed/dirty hands.
Pinworm eggs can be found on unwashed fruit or vegetables, or on the fur of a sick animal. Children who scratch itchy skin areas and then swallow eggs (for example, along with contaminated food) are more likely to become infected with enterobiasis. It takes two weeks to develop pinworm larvae in the environment of the digestive tract, and after full development, a full-fledged worm lives in all parts of the large intestine.
Trichinella: These parasites have round bodies no more than 5mm in length and cause trichinosis in the body. Larvae and eggs prefer to be in poorly fried meat (boar, pork, bear meat). In the human body, Trichinella takes up to 4 days to become an adult and its life cycle is 40 days. The main goal of this type of worm is to enter the bloodstream through the intestinal walls and settle in the muscles. In addition, the muscles of the respiratory and musculoskeletal systems are often affected.
Roundworms are representatives of large sizes, which are spindle-shaped with a red-yellow tint. Males of this species reach a size of 15-25 cm, and females - up to 40 cm. Their body lacks adaptations for fixing in the intestine, they only move independently to the mass of food through the intestines.
You can get infected with roundworms by swallowing ripe eggs when eating unwashed vegetables or fruits, on which the smallest particles of soil remain. After the eggs enter the internal environment of the body, the adult larvae hatch from them, terrorizing the intestinal walls. Through the bloodstream, the parasites can reach the heart muscle and then the lungs.
Only at this the cycle of travel through the body does not end, because the larva moves through the respiratory tract to the mouth.
By re-swallowing the parasite, the body already creates a favorable environment for its development.
The route of a full-fledged worm will go through the small intestine. Their life cycle is 12 months, then they die and are excreted in the feces.
Vlasoglavy - worms in humans, the symptoms and treatment of which are determined at any time after infection, preferring to live directly in the intestines. This worm eats the blood component or feeds on the intestinal mucosa.
The females lay eggs directly on the walls of the affected organ, then they come out together with the feces and develop in ambient conditions. An already mature larva, the body of which is oblong, and does not exceed the limits of 5-15 mm. enters the human body alimentary.
These parasites have round bodies no more than 5 millimeters long and cause trichinosis in the body. Larvae with eggs are found in poorly fried meat (boar, pork, bear meat).
In the human body, Trichinella takes a maximum of 4 days to become an adult and its life cycle does not exceed 40 days. The main goal of this type of worm is to enter the bloodstream through the intestinal walls and settle in the muscles. In addition, the muscles of the respiratory and musculoskeletal systems are often affected.
Necator/hookworm. The connection between these parasites is direct, in relation to the ailments they cause and the biological signs. They live in the duodenum and due to their small size (10-15 mm) they move freely in their environment.
The larvae can enter the body only through the skin if a person has been in contact with contaminated soil. Another target of the worms is the lungs along with the digestive tract. They feed solely on the blood that comes out of bitten blood vessels. As a result of the violent activity of these parasites, blood coagulation is disturbed. Adults consume blood in the range of 0. 1-0. 35 ml per day.
varieties of flatworms
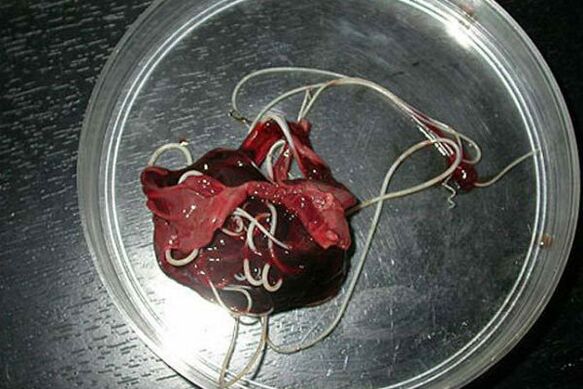
wide ribbonThe length of the body of the parasite, which is 10 to 20 meters, deserves attention.
The parasite originates from freshwater fish and crayfish, the larvae enter eggs and fish fillets.
The formation of an adult worm takes a maximum of 25 days, and then a person becomes ill with diphyllobothriasis (the digestive tract is disturbed, vitamin B deficiency).
Liver fluke is a flatworm that reaches a size of 10-20 mm, and there is a second name for this parasite - cat fluke. In 50% of cases of infection, residents who have consumed infected fish (carp, crucian carp, bream, roach) suffer. Fish are infected with liver flukes through a consumed snail that has previously consumed helminth eggs with fresh water.
To clean the fish from the parasite, heat treatment is necessary, otherwise the larva will enter the internal environment of the body and damage the gallbladder with the intestines. Signs of the acute phase of the development of helminthiasis in humans are a feeling of nausea turning into vomiting, pain in the upper abdomen, allergic reactions, muscle spasms. The parasite creates irreversible changes in the body, and even after its expulsion from the patients' body, all kinds of inflammations and disorders are sure to occur.
Porcine/bovine tapeworm. The body length of the parasite is 5-6 meters, and its larvae hide in the meat of large animals (pig, cattle). The disease caused by these helminths is called taeniasis and teniarinhoz.
The larvae of both species of tapeworm, the Finnish, are whitish vesicles attached to the walls of the small intestine. To reach and form an adult, the parasite needs 3 months, and every day the worm develops. The total number of segments reaches 2000, the end of which freely "furrows" the large intestine.
The worms then leave the body along with feces through the anus. The most common and obvious symptom of helminthiasis is a disturbed digestive tract, as well as food intake in large volumes, and the patient does not visually gain weight.
Echinococcus. In this case, a person acts as an intermediate host, because the latter are wolves, cats, dogs. Animals can become infected through direct contact with contaminated people or objects. As soon as the eggs of the parasite enter the intestines, larvae with six hooks immediately develop, which in medicine are called oncospheres.
The favorite habitat of the worm is the lungs and liver, and the larva develops into an echinococcus cyst, increasing in size. All tissues near him are subject to rapid destruction.
Doctors often miss echinococcosis and confuse it with a malignant or benign formation. In addition to squeezing blood vessels and internal organs, echinococcus cyst ruptures are common.
If this happens, not only does a toxic shock immediately occur in the body, but one ruptured cyst causes the formation of several new ones.
The last type of parasite is the alveococci, in the medical literature they are called echinococci. It is this worm that awakens a terrible disease that causes damage comparable to cancer and cirrhosis of the liver. The oncospheres of the worm enter the intestines, then the embryos hatch from the eggs and begin to destroy the intestinal walls. After piercing the walls, the parasite enters the bloodstream and spreads throughout the body.
Most often, as mentioned above, alveococci terrify the liver, where the larva gradually grows. In the process of development, the larvocyst is formed in worms - an aggressive formation that rapidly increases in size (a gradually growing multi-chambered vesicle). These vesicles make their way to liver cells, following the same principle as cancerous metastases.
Nearby tissues feel a violation of blood flow, and then necrotic changes occur in them. Fibrous nodules with such multichamber blisters form on nearby structures and can remain on the human body for several years. That is why doctors, detecting this parasite, resort to surgical intervention.
Note
Modern science knows about 280 species of worms. It is these microorganisms that can parasitize and develop in a variety of tissues and organs of the human body.
Every year, these worms in humans, the symptoms and treatment of which are determined by the doctor, affect the organs and tissues of about 15 million people, and the majority, to be more precise, 80% of them are children.
How can you get worms?
- The use of meat dishes with poor heat treatment or raw meat in general. So, beef is the habitat of the tapeworm, and the pig carries the pork tapeworm.
- Consumption of infected fish in slightly salted or raw form. River water is often contaminated with helminth larvae.
- Water can also cause worms. This is due to the fact that a person can drink raw water or wash food, dishes with contaminated water. The risk is especially high when you are outdoors.
- The soil can also cause the appearance of worms. Because it may contain animal or human feces. But how do worms enter the human body? The answer is simple: through dirty hands after gardening or outdoor recreation.

Also, you can become infected through direct contact with a person who has helminthiasis. That is, the infection occurs through dishes, bedding or personal hygiene items.
If the case is completely neglected, and the parasitic infection is in the acute phase of its development, doctors prescribe detoxification and desensitization therapy. And if the disease is very difficult, glucocorticoids are prescribed.
Speaking of specific therapy, it takes into account the nature of the pathogen and involves special chemotherapeutic agents of an anthelmintic nature.
In addition, patients are recommended to take various antihistamines. At the end of treatment, you will need to take a course of probiotics. All this is necessary to restore the intestinal microflora. In the process of treatment, the patient must follow a special diet, which consists of easily digestible foods with a minimum fat content.
At the time of therapy, it is very important to comply with impeccable personal hygiene, otherwise there is a risk of reinfection.
Also, all family members, as well as other people who were in constant and close contact with the patient, must undergo anthelmintic treatment.
Signs of worms in humans: symptoms in children and adults.
Signs of worms in humans, the symptoms of which may be the same, can be observed acutely, both in adults and in children:
- Unreasonable increase in appetite and profuse salivation, and at the same time, rapid weight loss.
- Another variant of the development of symptoms may also occur: the appetite disappears, after eating the person feels sick.
- Perhaps the appearance of headaches and dizziness.
- Loose stools or constipation can also indicate the presence of worms.
- Pain in the abdomen.
- Sudden onset of an allergy with incomprehensible symptoms.
- Weakening of hair and nails (increases their fragility due to lack of iron and vitamin B12).
- Due to the weakening of the immune system, various inflammations appear in the nasopharynx and in the genital area.
If the body is heavily infected with worms, then a large number of toxic substances that appear due to the vital activity of helminths are released into the human blood. This circumstance can greatly affect the health of the child. First of all, the nervous system suffers. Therefore, if a child shows sudden aggressiveness, irritability, insomnia and other signs of nervous disorders, the child should be checked for the presence of helminths.

Even if there are no pronounced signs and there are no functional disorders, worms may be present in the human body, and periodic testing is necessary to identify them.
Very often it happens that after preventive vaccinations, a child develops an allergic reaction due to the presence in the body of toxic substances secreted by helminths.
In fact, determining whether or not there are worms based solely on superficial signs is quite a difficult task. After all, the symptoms that are displayed may be a sign of another disease. This task is especially difficult for pregnant women. Since all the above signs of worms in humans, the symptoms of which were described above, in pregnant women they appear due to the process itself.
For this reason, signs of helminth infection in pregnant women can be distinguished by such symptoms: itching in the anus and burning in the vaginal area, which increase at night, weight loss, fatigue, fever.
To diagnose helminth infection, a number of measures are carried out, which include the following procedures:
- Collection of an anamnesis to identify possible sources of infection.
- The study of stool and blood samples, rectal and perianal mucus, muscle tissue, sputum, and bile in the laboratory. When carrying out these activities, signs of the presence of helminths in the body (eggs or the worms themselves, as well as their parts) can be detected. It is also worth noting that an increased number of eosinophils can serve as a sign of the presence of worms in the body.
- Serological studies (ELISA, RSK, etc. ) allow detecting the presence of parasites in the larval stage or helminths that live in muscle tissues.
- To determine the presence of parasites that affect the liver, ultrasound, computed tomography and endoscopy are prescribed.
Worms in the human liver: symptoms by type of worm
Worms in the human liver, the symptoms of which largely depend on the type of helminths, can also migrate to other organs.
The appearance of primary signs of infection with worms does not appear immediately. In many ways, the timing of appearance of distinctive features depends on the species composition of the parasites. So, the presence of ascaris in almost two or three days is manifested by a deterioration in the general condition of a person.
The first symptoms of infection with other types of helminths in most cases begin to appear only two to three weeks after the end of the incubation period. There are such parasites (for example, filariasis) in which the incubation period exceeds six months.
The problem with determining the presence of helminths in the human body is that in the case of primary infection with a small number of worms or a single individual, there are practically no visual signs. Symptoms begin to appear only after intensive reproduction of helminths or when they reach large sizes (broad tapeworm, pinworm).
It is more reliably possible to determine the infection with pinworms. In their presence a characteristic itching appears in the anus, which intensifies at night. Basically, the itchiness occurs in a couple of days, then it goes away for about two weeks and picks up again.
When infected with helminths such as trichuriasis, hookworm, schistosomiasis, diphyllobothriasis, beriberi, and anemia develop.
The appearance of symptoms of roundworm infection largely depends on the period of development of the parasites. So, if they are in the initial stage of development, the larvae move through the blood to almost all internal organs, and the following symptoms of the disease appear: subfebrile temperature, weakness, cough with purulent sputum, volatile infiltrates are visible in X-rays of the lungs, which subsequently disappear.
With a severe infection, bronchitis and pneumonia can develop. With further development of parasites, there is a violation of the functions of the gastrointestinal tract.
Trichinosis: mainly manifests its presence with pain in muscle tissues, fever and swelling.
Such worms in the human liver, the symptoms of which are manifested by a jaundiced complexion, such as fascioliasis, opisthorchiasis, clonorchiasis, reveal their presence with an increase in the spleen and liver and other serious disorders of the body.
Almost all types of worms cause central nervous system disorders, while the sick person feels severe headaches and fatigue, a usually calm person becomes irritable and impatient, and irrational bouts of aggression may appear.






































